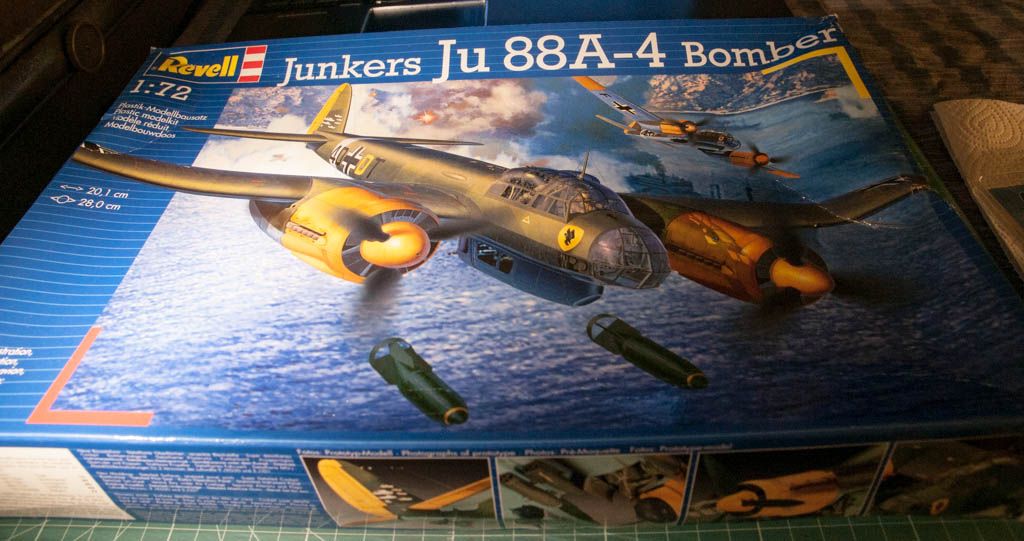
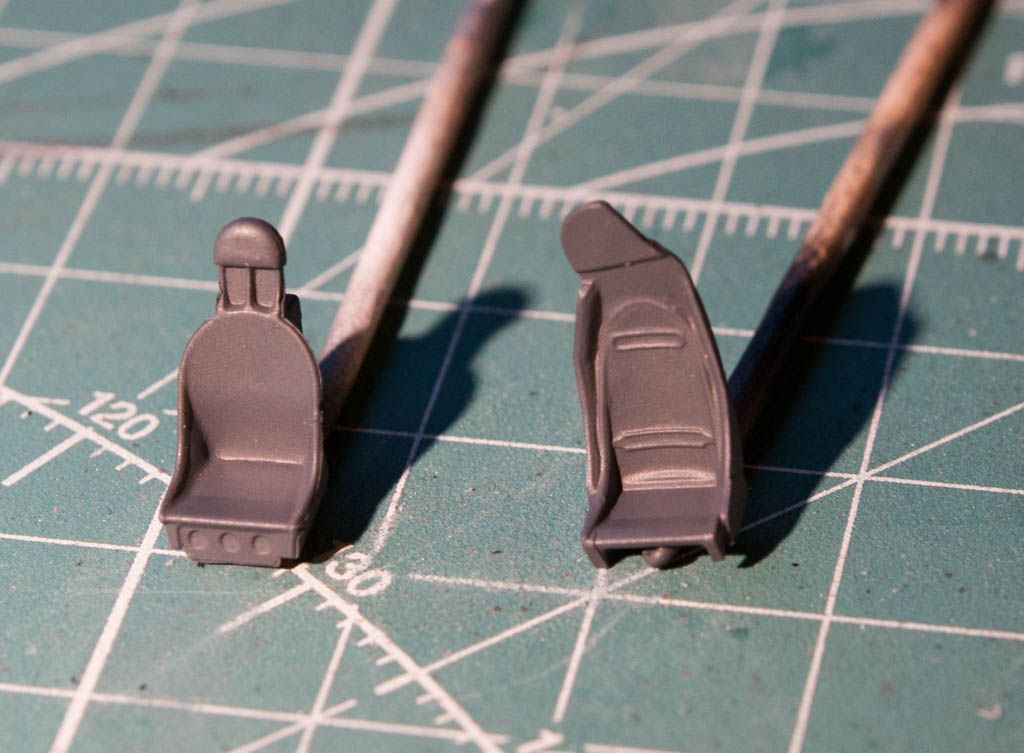
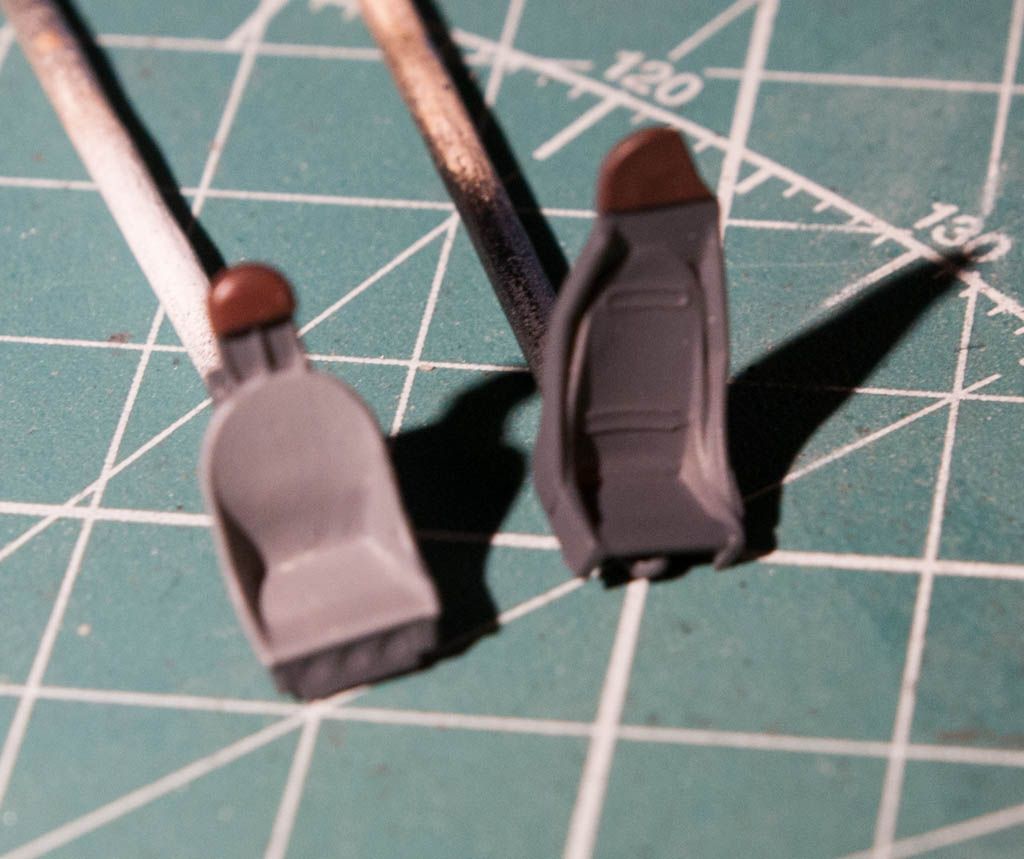
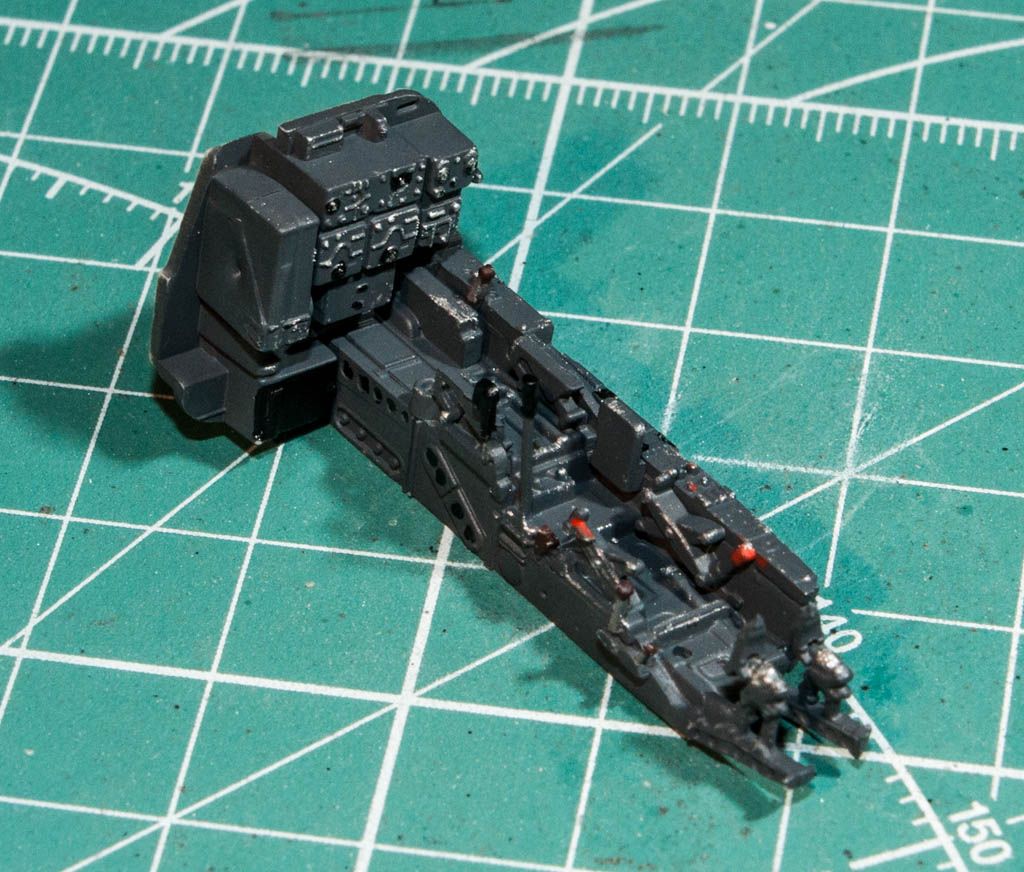
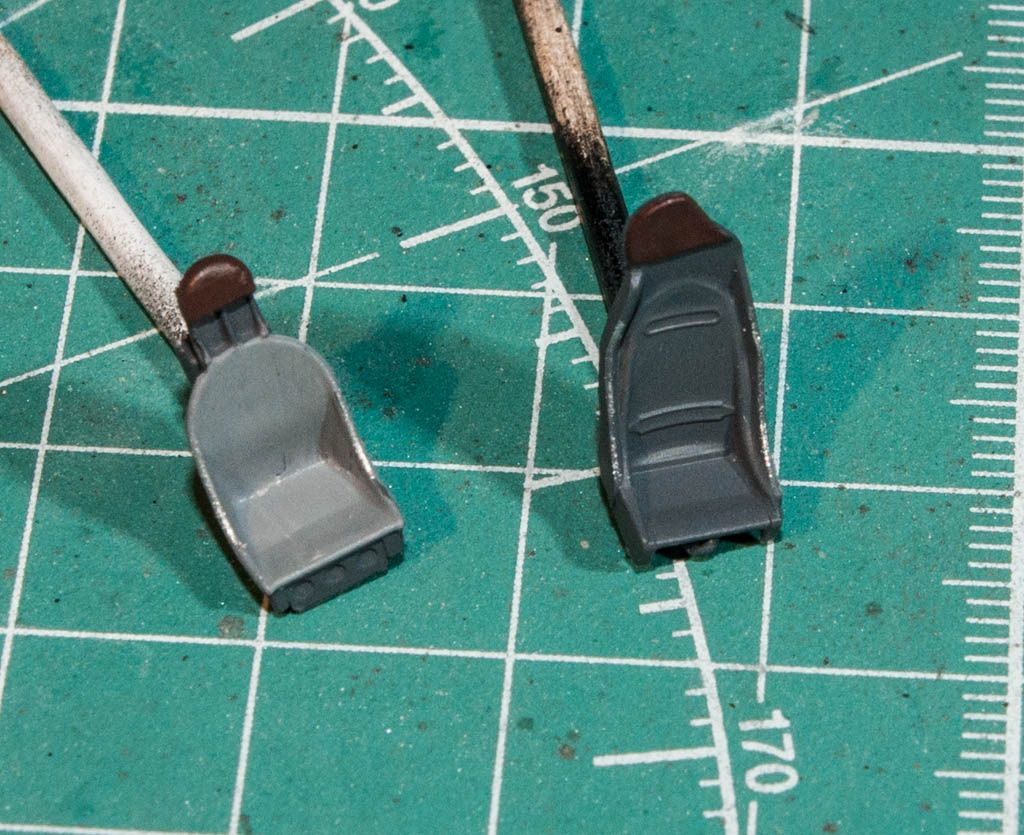
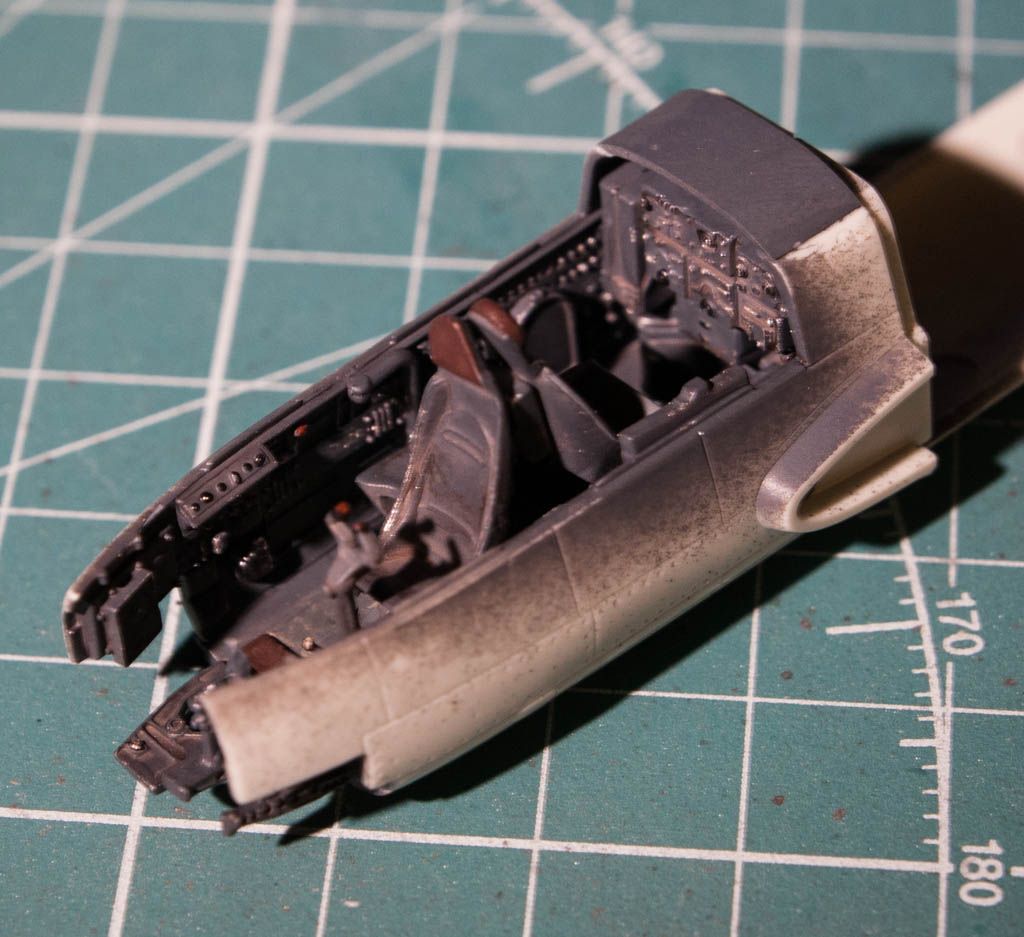
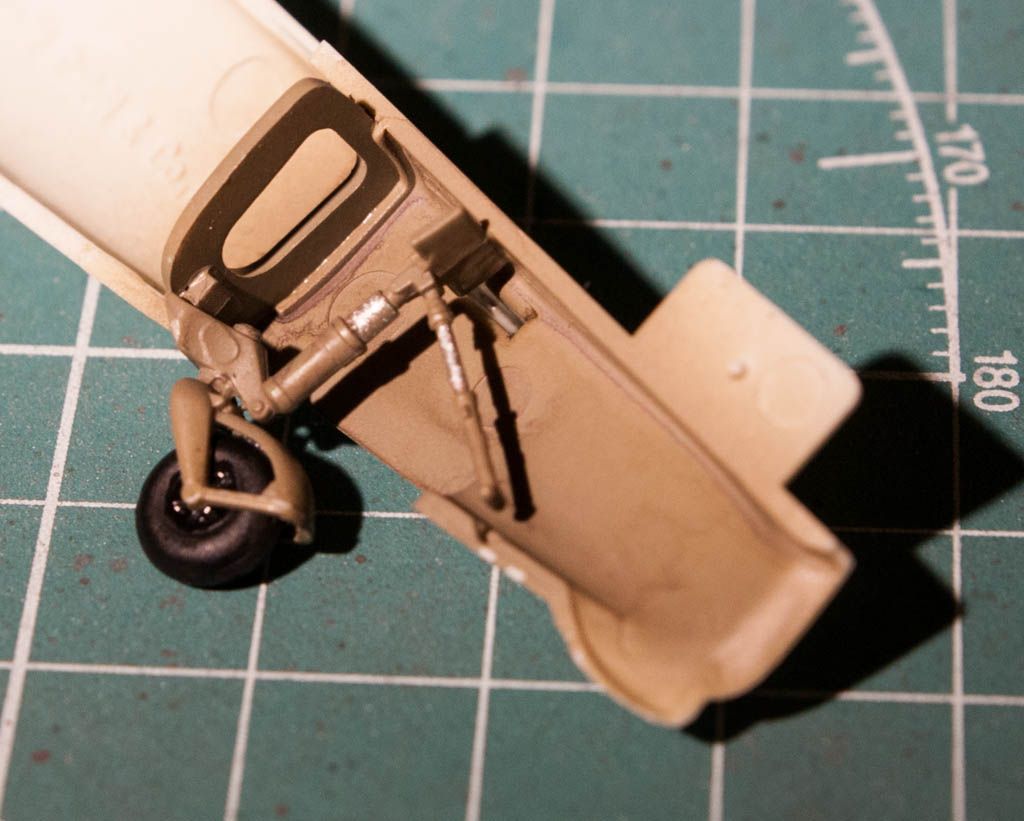
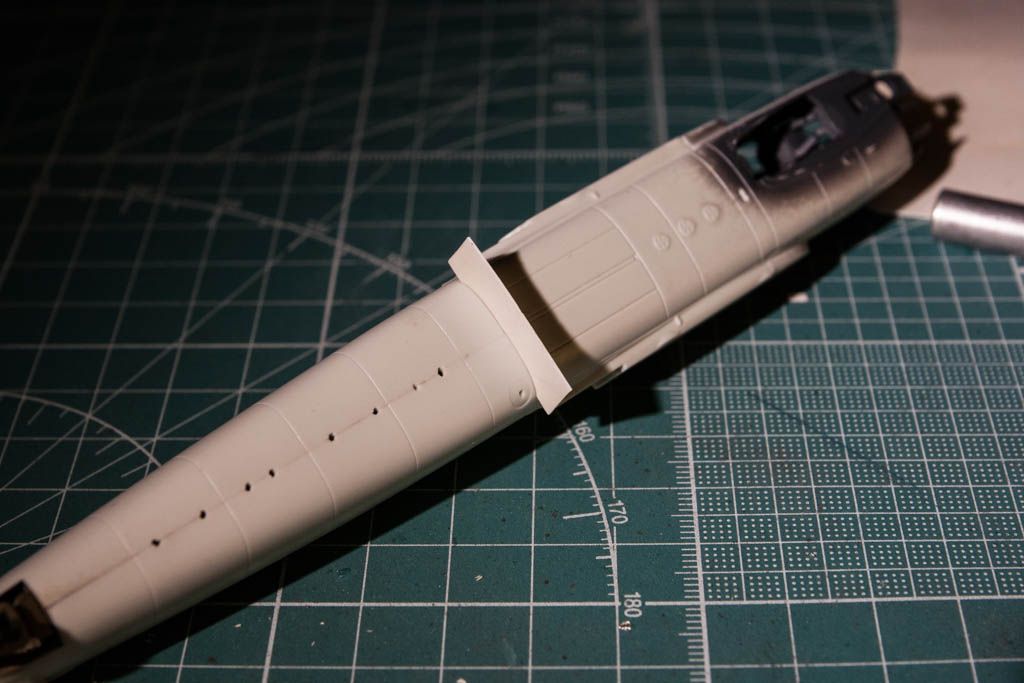
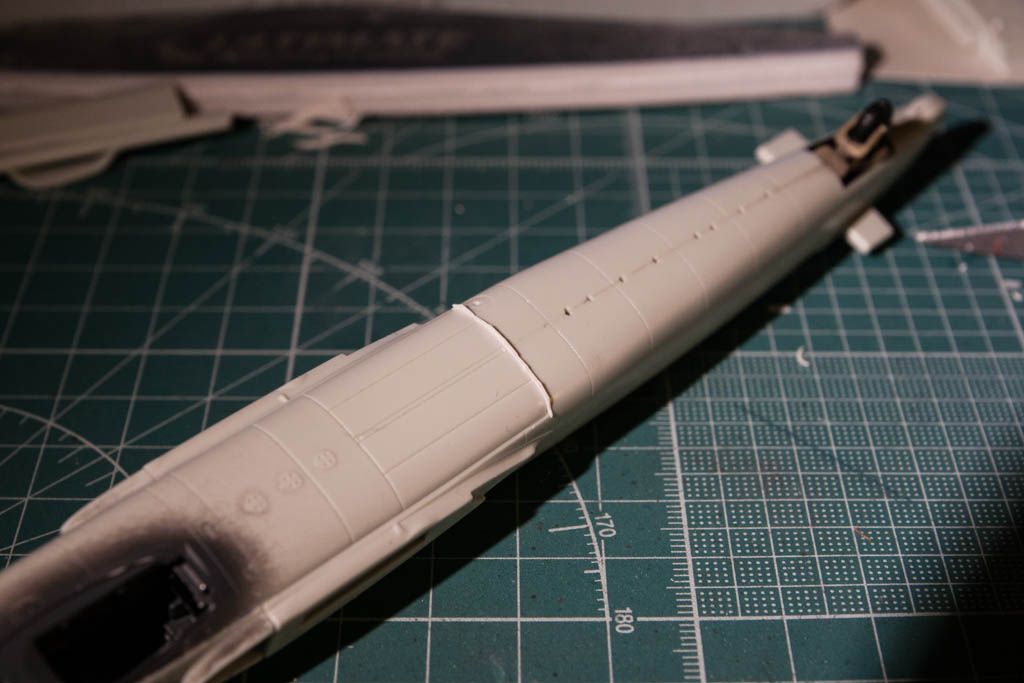
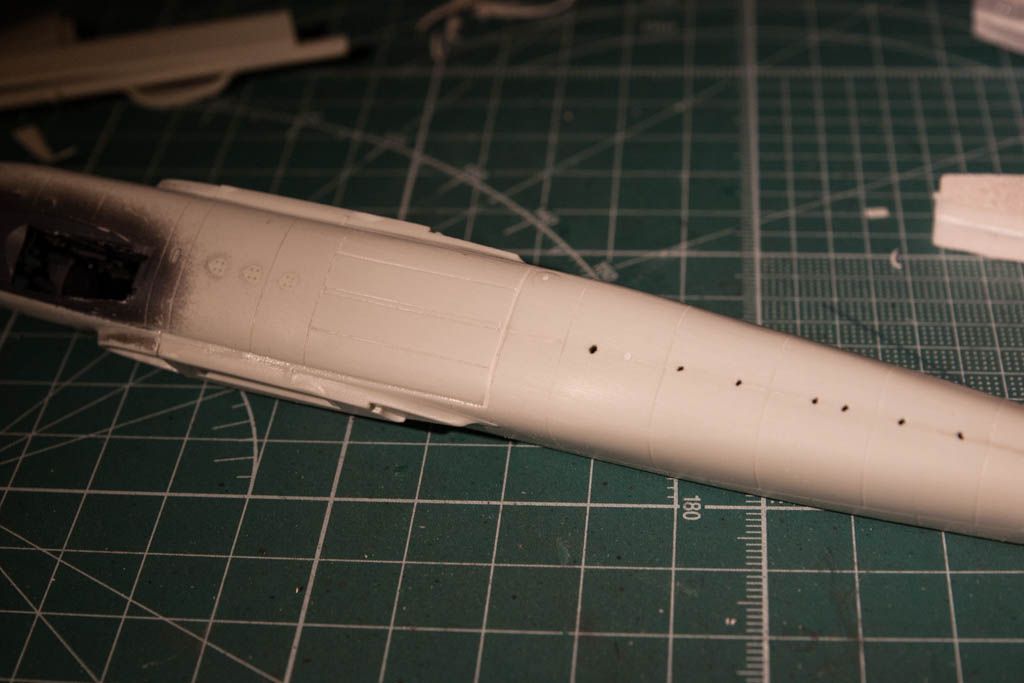
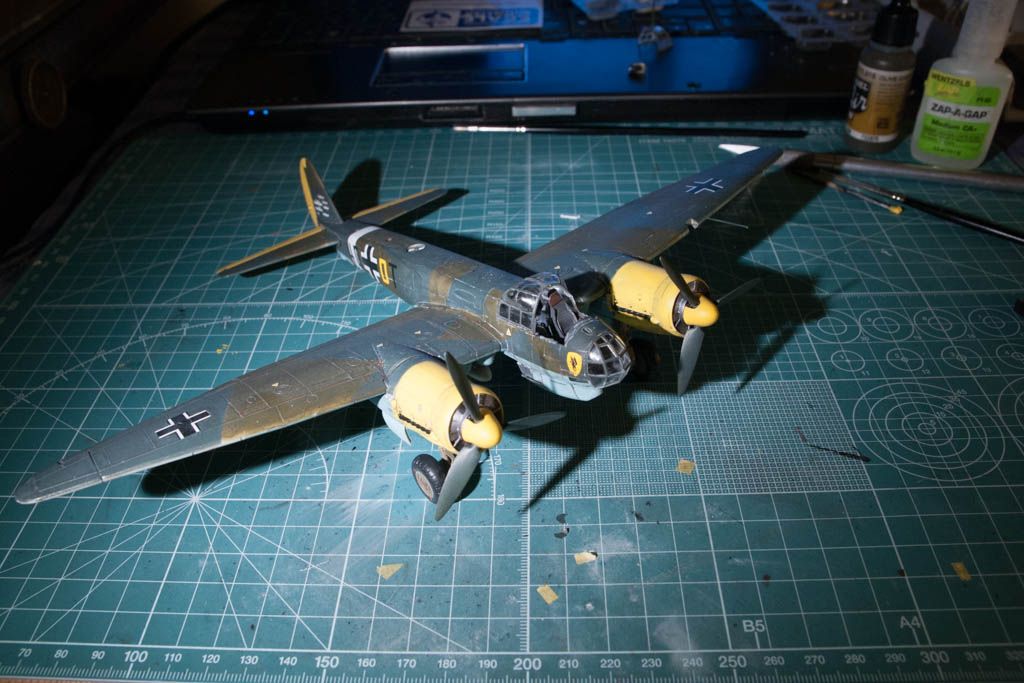
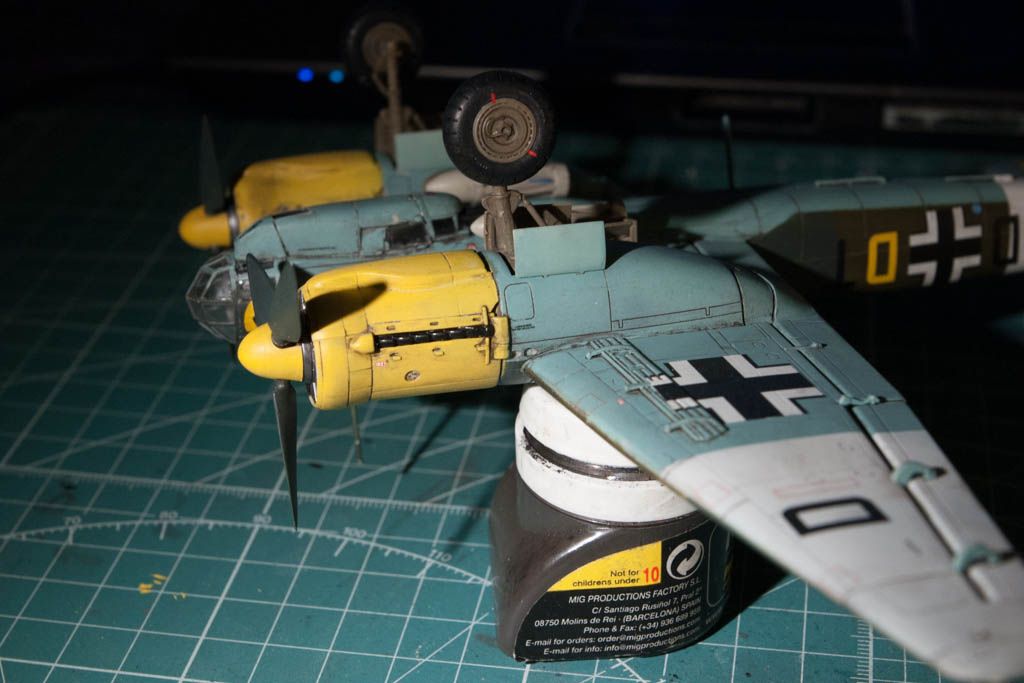
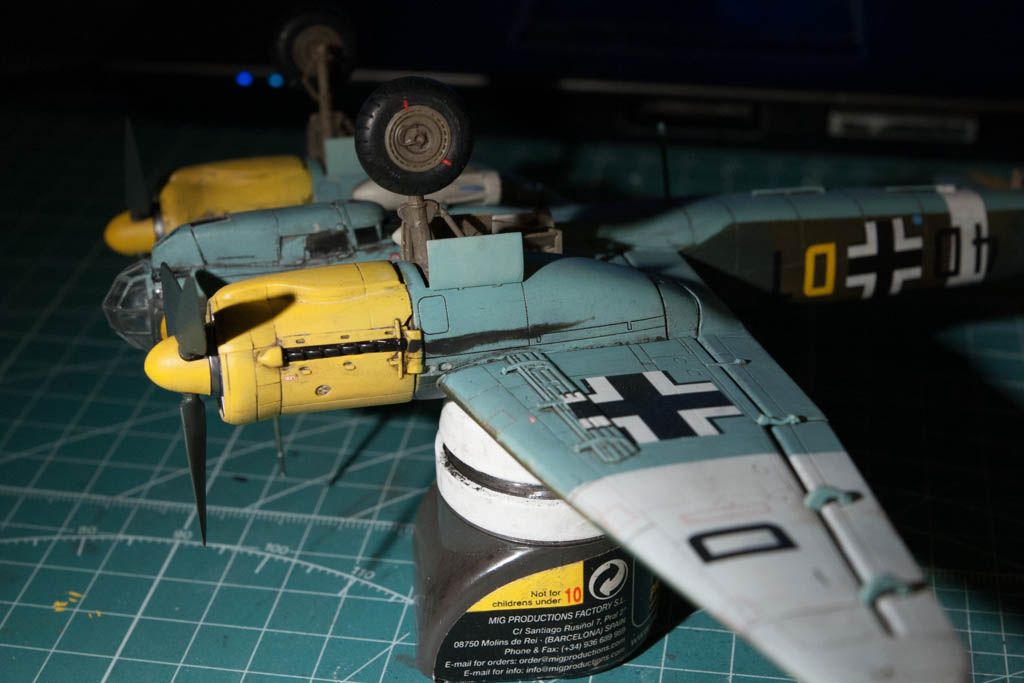
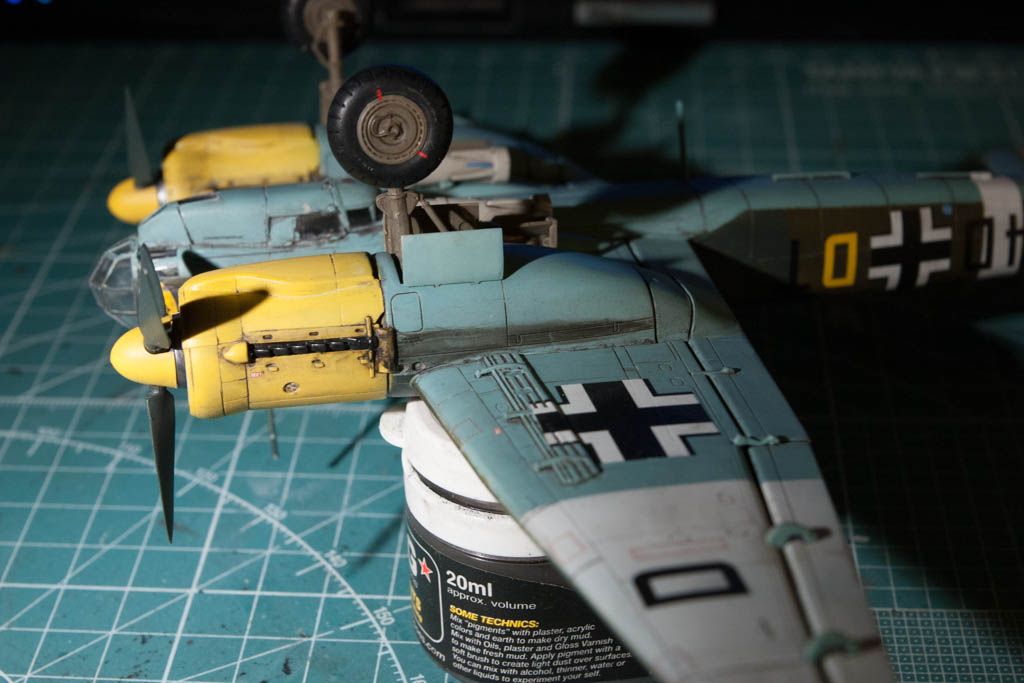
So a bit of info on the plane:
It has wings and it flies.
Sorry I'm a car guy and have no idea about flying things.

Luckily Wikipedia knows a bit more.
Junkers Ju 88
Role: Dive bomber/Tactical bomber/Night fighter/Torpedo bomber/Heavy fighter
Manufacturer: Junkers
Designer: W. H. Evers and Alfred Gassner
First flight: 21 December 1936
Introduction: 1939
Retired: 1951 (France)
Primary user: Luftwaffe
Number built: 15,183
Variants: Junkers Ju 188

The Junkers Ju 88 was a World War II German Luftwaffe twin-engine, multi-role aircraft. Designed by Hugo Junkers' company in the mid-1930s to be a so-called Schnellbomber which would be too fast for any of the fighters of its era to intercept, it suffered from a number of technical problems during the later stages of its development and early operational roles, but became one of the most versatile combat aircraft of the war. Affectionately known as "The Maid of all Work" (Mädchen für Alles), the Ju 88 proved to be suited to almost any role. Like a number of other Luftwaffe bombers, it was used successfully as a bomber, dive bomber, night fighter, torpedo bomber, reconnaissance aircraft, heavy fighter, and even as a flying bomb during the closing stages of conflict.
Despite its protracted development, the aircraft became one of the Luftwaffe's most important assets. The assembly line ran constantly from 1936 to 1945, and more than 16,000 Ju 88s were built in dozens of variants, more than any other twin-engine German aircraft of the period. Throughout the production, the basic structure of the aircraft remained unchanged.
Design and development
The Ju 85 was a twin-engined bomber aircraft prototype, designed by Junkers in 1935. The Reich Air Ministry requested the aircraft, which differed from the Ju 88 due to the use of a twin fin tail unit. The aircraft was never put into service.
In August 1935, the German Ministry of Aviation submitted its requirements for an unarmed, three-seat, high-speed bomber, with a payload of 800-1,000 kg (1,760-2,200 lb). Junkers presented their initial design in June 1936, and were given clearance to build two prototypes (Werknummer 4941 and 4942).[6] The first two aircraft were to have a range of 2,000 km (1,240 mi) and were to be powered by two DB 600s. Three further aircraft, Werknummer 4943, 4944 and 4945, were to be powered by Jumo 211 engines. The first two prototypes, Ju 88 V1 and V2, differed from the V3, V4 and V5 in that the latter three models were equipped with three defensive armament positions to the rear of the cockpit, and were able to carry two 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) bombs, one under each inner wing panel.
The first five prototypes had conventionally operating dual-strut leg rearwards-retracting main gear, but starting with the V6 prototype, a main gear design debuted that twisted the new, single-leg main gear strut through 90° during the retraction sequence, much like that of the American Curtiss P-40 Warhawk fighter. This feature allowed the main wheels to end up above the lower end of the strut when fully retracted and was adopted as standard for all future production Ju 88s, and only minimally modified for the later Ju 188 and 388 developments of it. These single-leg landing gear struts also made use of stacks of conical Belleville washers inside them, as their main form of suspension for takeoffs and landings.
By 1938, radical modifications from the first prototype began to produce a "heavy" dive bomber. The wings were strengthened, dive brakes were added, the fuselage was extended and the number of crewmen was increased to four. Due to these advances, the Ju 88 was to enter the war as a medium bomber.

The choice of annular radiators for engine cooling on the Ju 88, which placed these radiators immediately forward of each engine and directly behind each propeller, allowed the cooling lines for the engine coolant and oil-cooling radiators (integrated within the annular design) to be just about as short as possible. The concept may have led to a number of other German military aircraft designs adopting the same solution, such as the Arado Ar 240, Heinkel He 177, Heinkel He 219, the inline powered developments of the Focke-Wulf Fw 190 and the twin-engined Focke-Wulf Ta 154.
The aircraft's first flight was made by the prototype Ju 88 V1, which bore the civil registration D-AQEN, on 21 December 1936. When it first flew, it managed about 580 km/h (360 mph) and Hermann Göring, head of the Luftwaffe was ecstatic. It was an aircraft that could finally fulfill the promise of the Schnellbomber, a high-speed bomber. The streamlined fuselage was modeled after its contemporary, the Dornier Do 17, but with fewer defensive guns because the belief still held that it could outrun late 1930s-era fighters. The fifth prototype set a 1,000 km (620 mi) closed-circuit record in March 1939, carrying a 2,000 kg (4,410 lb) payload at a speed of 517 km/h (320 mph). However, by the time Luftwaffe planners like Ernst Udet had their opportunities to their own "pet" features added (including dive-bombing by Udet), the Ju 88's top speed had dropped to around 450 km/h (280 mph). The Ju 88 V7 was fitted with cable-cutting equipment to combat the potential threat of British barrage balloons, and was successfully tested in this role. The V7 then had the Ju 88 A-1 "beetle's eye" faceted nose glazing installed, complete with the Bola undernose ventral defensive machine gun emplacement, and was put through a series of dive-bombing tests with 250 kg (550 lb) and 500 kg (1,100 lb) bombs, and in early 1940, with 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) bombs. The Ju 88 V8 (Stammkennzeichen of DG+BF, Wrk Nr 4948) flew on the 3 October 1938. The A-0 series was developed through the V9 and V10 prototypes. The A-1 series prototypes were Wrk Nrs 0003, 0004 and 0005. The A-1s were given the Jumo 211B-1 or G powerplants.
Dr. Heinrich Koppenberg (managing director of Jumo) assured Göring in the autumn of 1938 that 300 Ju 88s per month was definitely possible. Göring was in favour of the A-1 variant for mass production.
Production was delayed drastically by developmental problems. Although planned for a service introduction in 1938, the Ju 88 finally entered squadron service (with only 12 aircraft) on the first day of the attack on Poland in 1939. Production was painfully slow, with only one Ju 88 manufactured per week, as problems continually kept cropping up. The Ju 88C series of heavy fighter was also designed very early in 1940, but kept secret from Göring, as he only wanted bombers.
Ju 88 A-4 Specifications
 General characteristics
Crew:
General characteristics
Crew: 4 (pilot, bombardier/front gunner, radio operator/rear gunner, navigator/ventral gunner)
Length: 14.36 m (47 ft 2⅞ in)
Wingspan: 20.08 m (65 ft 10½ in)
Height: 5.07 m (16.63 ft)
Wing area: 54.7 m2 (587 ft2)
Loaded weight: 8,550 kg (18,832 lb)
Max. takeoff weight: 14,000 kg[61] (30,865 lb)
Powerplant: 2 × Junkers Jumo 211J[62] liquid-cooled inverted V-12, 1,044 kW (1,420 PS, 1,401 hp) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 510 km/h[61] (317 mph) at 5,300 m (17,389 ft) without external bomb racks or 433 km/h (269 mph) at 4,500 m (14,765 ft) at 14,000 kg (30,865 lb)
Range: 2,430 km[61] (1,429 mi)maximum internal fuel
Service ceiling: 9,000 m (29,500 ft) at average weight, without bombs
Rate of climb: 235 m/min (770 ft/min)
Armament
Guns:
1 × 7.92 mm MG 81J machine gun on flexible mount in front windscreen, firing forward with 1,000 rounds.[N 3]
1 × 7.92 mm MG 81J machine gun on flexible mount in lower fuselage nose glazing, firing forward with 1,000 rounds.
2 × 7.92 mm MG 81J machine guns on flexible mount in the rear of the cockpit canopy, firing aft with 1,000 rounds each.[63]
1 × 7.92 mm MG 81Z twin machine gun on flexible mount in the rear ventral Bola position, firing aft with 1,000 rounds.[61][63]
Bombs: Up to 1,400 kilograms (3,100 lb) of ordnance internally in two bomb bays rated at 900 kg (2,000 lb) and 500 kg (1,100 lb) or up to 3,000 kg (6,600 lb) externally. Carrying bombs externally increased weight and drag and impaired the aircraft's performance. Carrying the maximum load usually required rocket-assisted take-off.
Armament options
Additional option for a pair of 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 15 machine guns on flexible "Donut" mountings firing laterally, one on each side of the cockpit canopy.
A single 13 mm (.51 in) MG 131 machine gun was sometimes used instead of the 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 81J or MG 81Z machine guns in the A-Stand, B-Stand or ventral Bola positions.
Aircraft may carry one 20 mm MG FF cannon in the nose for ground attack purposes, with 90 rounds of ammunition, in place of the Lotfernrohr 7 bombsight
A modification of the Ju 88 A-4, the Ju 88 A-13 could mount the Waffenbehälter WB 81A or WB 81B (firing with 15° downwards deflection) gun pods on the external bomb racks for ground attack duties, each "watering can" containing three 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 81Z twin machine guns, for strafing enemy troops.
[youtube]5EcZqLatu8E[/youtube]