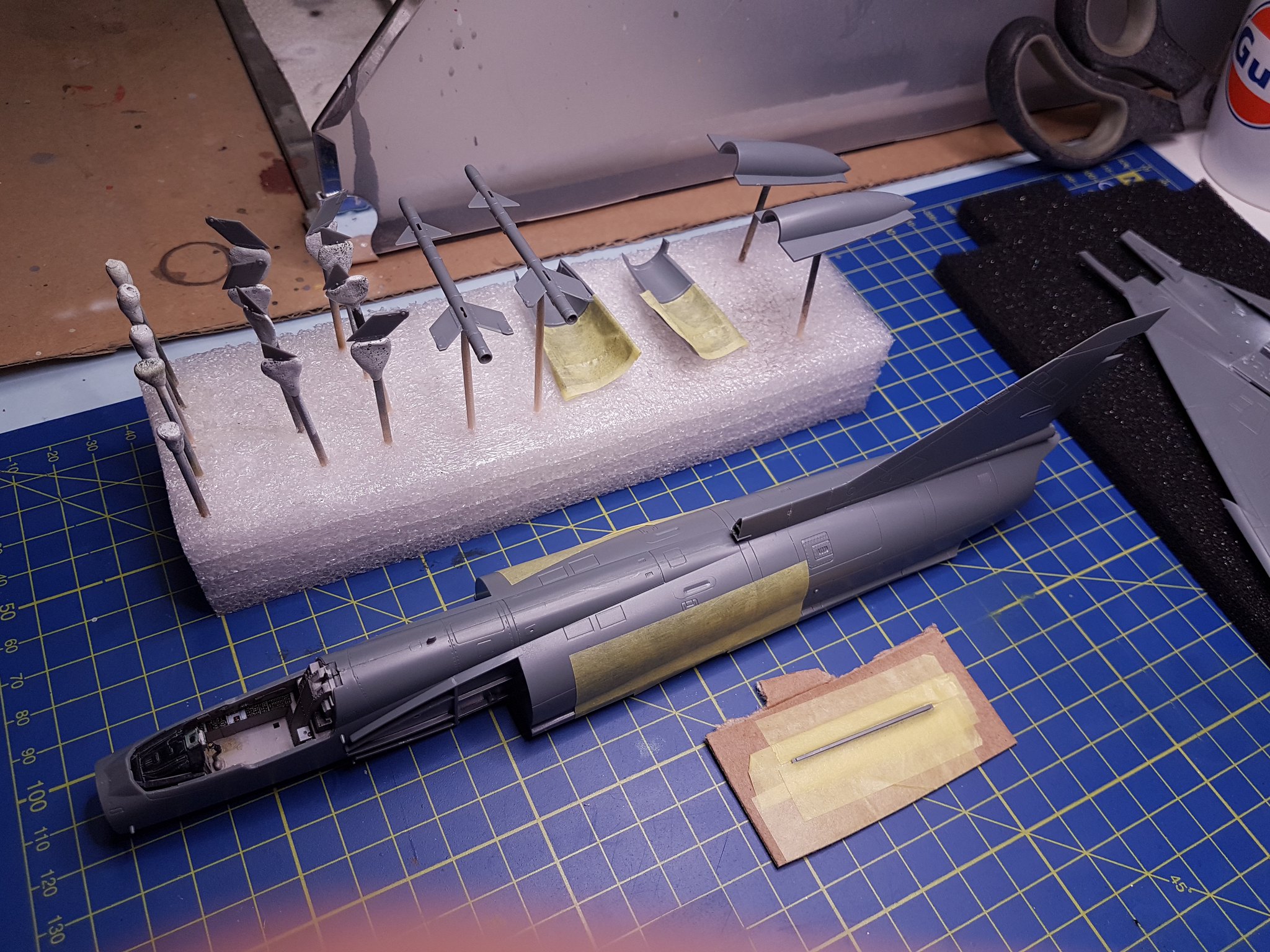
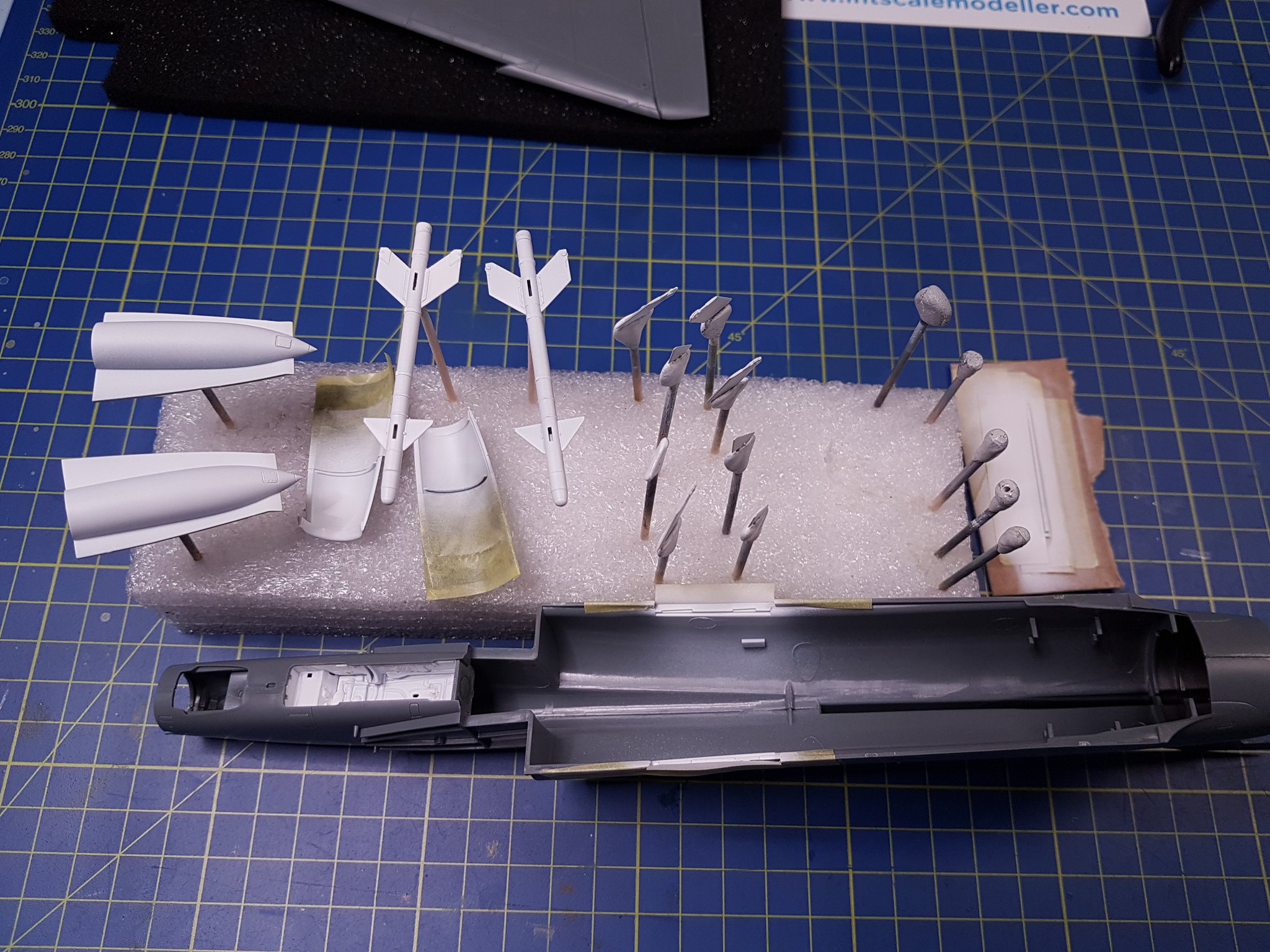
I will enter this SiG building the IAI Kfir.


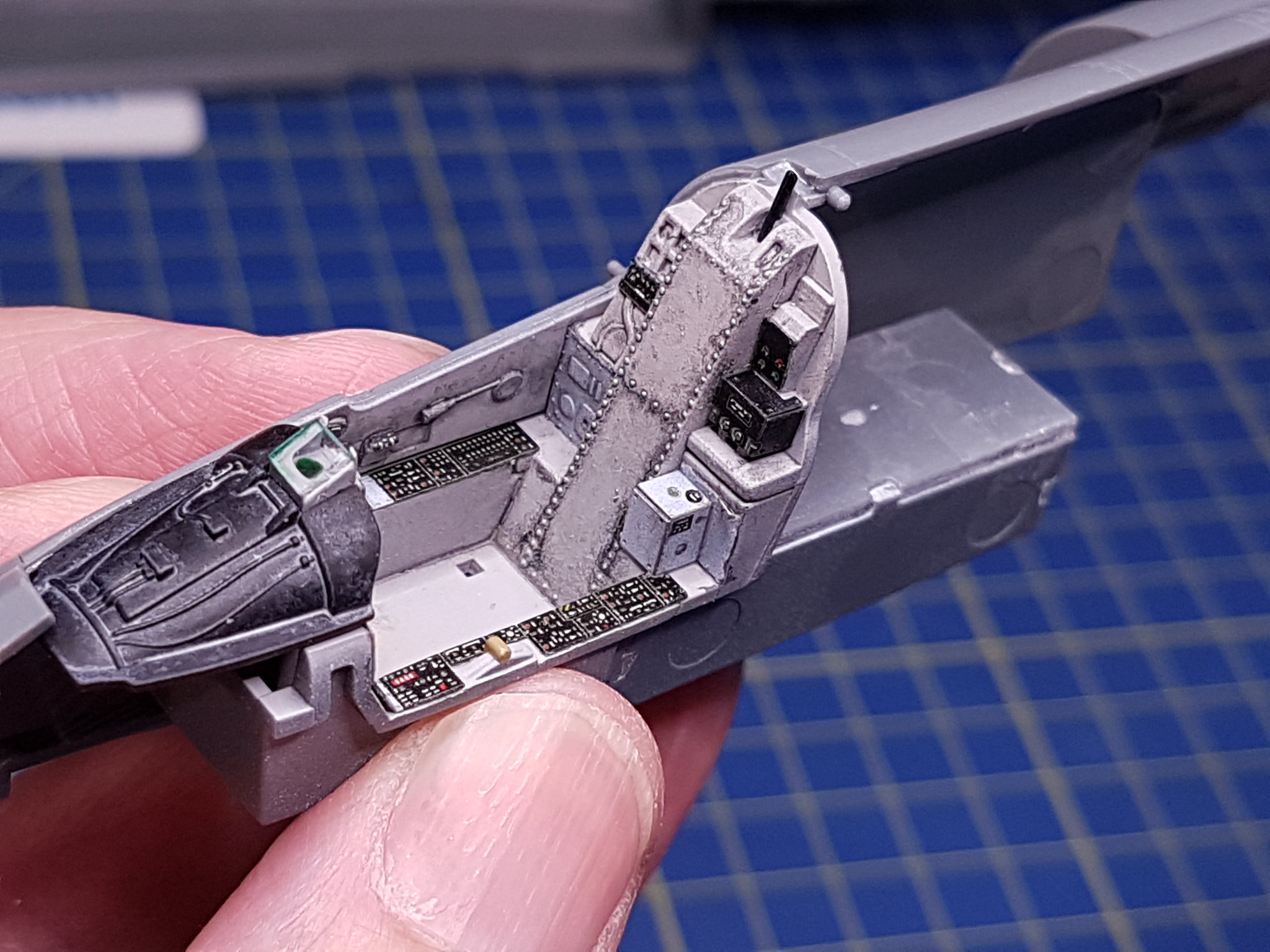
I will use the AMK 1/48 Kfir C2/C7 kit also adding some aftermarket, where I will build the C7 version of the aircraft
Boxart:
 IMG_20170701_085608 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr
IMG_20170701_085608 by Tommy Killander, on FlickrAssembly Instructions and aftermarket (Eduard Zoom kit, masking set and Master pitot-tube + Angle of Attack probe):
 IMG_20170701_085454 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr
IMG_20170701_085454 by Tommy Killander, on FlickrSprues:
 IMG_20170701_090201 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr
IMG_20170701_090201 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr IMG_20170701_090345 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr
IMG_20170701_090345 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr IMG_20170701_090841 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr
IMG_20170701_090841 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr IMG_20170701_090603 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr
IMG_20170701_090603 by Tommy Killander, on FlickrDecals and clear parts:
 IMG_20170701_085902 by Tommy Killander, on Flickr
IMG_20170701_085902 by Tommy Killander, on FlickrBackground:
The Israel Aircraft Industries Kfir (Hebrew: כְּפִיר, "Lion Cub") is an Israeli-built all-weather, multirole combat aircraft based on a modified French Dassault Mirage 5 airframe, with Israeli avionics and an Israeli-built version of the General Electric J79 turbojet engine.
The project that would ultimately give birth to the Kfir can be traced back to Israel's need for adapting the Dassault Mirage IIIC to the specific requirements of the Israeli Air Force (IAF).
The all-weather, delta-winged Mirage IIICJ was the first Mach 2 aircraft acquired by Israel from then close ally France, and constituted the backbone of the IAF during most of the 1960s, until the arrival of the Douglas A-4 Skyhawk and, most importantly, the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, by the end of the decade. While the Mirage IIICJ proved to be extremely effective in the air-superiority role, its relatively short range of action imposed some limitations on its usefulness as a ground-attack aircraft.
Thus, in the mid-1960s, at the request of Israel, Dassault Aviation began developing the Mirage 5, a fair-weather, ground-attack version of the Mirage III. Following the suggestions made by the Israelis, advanced avionics located behind the cockpit were removed, allowing the aircraft to increase its fuel-carrying capacity while reducing maintenance costs.
By 1968, Dassault had finished production of the 50 Mirage 5Js paid for by Israel, but an arms embargo imposed upon Israel by the French government in 1967 prevented deliveries from taking place. The Israelis replied by producing an unlicensed copy of the Mirage 5, the Nesher, with technical specifications for both the airframe and the engine obtained by Israeli spies. Some sources claim Israel received 50 Mirage 5s in crates from French Air Force (AdA), while the AdA took over the 50 aircraft originally intended for Israel.
Operational History:
The Kfir entered service with the IAF in 1975, the first units being assigned to the 101st "First Fighter" Squadron. Over the following years, several other squadrons were also equipped with the new aircraft. The role of the Kfir as the IAF's primary air superiority asset was short-lived, as the first F-15 Eagle fighters from the United States were delivered to Israel in 1976.
The Kfir's first recorded combat action took place on November 9, 1977, during an Israeli air strike on a training camp at Tel Azia, in Lebanon. The only air victory claimed by a Kfir during its service with the IAF occurred on June 27, 1979 when a Kfir C.2 shot down a Syrian MiG-21.
By the time of the Israeli invasion of southern Lebanon in 1982 (Operation Peace for Galilee) the IAF was able to use both its F-15s and F-16s for air superiority roles, leaving the Kfirs to carry out unescorted strike missions. Shortly afterwards, all IAF C.2s began to be upgraded to the C.7 version, with enhanced weight performance, making the Kfir more suitable to its new fighter-bomber role. During the second half of the 1990s, the Kfirs were withdrawn from active duty in the IAF, after almost twenty years of continuous service.
Specifications:
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 15.65 m (51 ft 4¼ in)
- Wingspan: 8.22 m (26 ft 11½ in)
- Height: 4.55 m (14 ft 11¼ in)
- Wing area: 34.8 m² (374.6 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 7,285 kg (16,060 lb)
- Loaded weight: 11,603 kg (25,580 lb) two 500 L drop tanks, two AAMs
- Max. takeoff weight: 16,200 kg (35,715 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × IAl Bedek-built General Electric J-79-J1E turbojet
- Dry thrust: 52.9 kN (11,890 lb st)
- Thrust with afterburner: 79.62 kN (17,900 lb st)
- Maximum speed: 2,440 km/h (2 Mach, 1,317 knots, 1,516 mph) above 11,000 m (36,000 ft)
- Combat radius: 768 km (415 nmi, 477 mi) (ground attack, hi-lo-hi profile, seven 500 lb bombs, two AAMs, two 1,300 L drop tanks)
- Service ceiling: 17,680 m (58,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 233 m/s (45,950 ft/min)
- Guns: 2× Rafael-built 30 mm (1.18 in) DEFA 553 cannons, 140 rounds/gun
- Rockets: assortment of unguided air-to-ground rockets including the Matra JL-100 drop tank/rocket pack, each with 19× SNEB 68 mm rockets and 66 US gallons (250 liters) of fuel
- Missiles: 2× AIM-9 Sidewinders or Shafrir or Python-series AAMs; 2× Shrike ARMs; 2× AGM-65 Maverick ASMs
- Bombs: 5,775 kg (12,730 lb) of payload on nine external hardpoints, including bombs such as the Mark 80 series, Paveway series of LGBs, Griffin LGBs, SMKBs,[35] TAL-1 OR TAL-2 CBUs, BLU-107 Matra Durandal, reconnaissance pods or Drop tanks
Tommy